
Square Kilometre Array–India Consortium (SKAIC): Scientific Literacy Through Radio Astronomy
This paper examines the Education and Public Outreach (EPO) initiatives by the Square Kilometre Array–India Consortium (SKAIC), aimed at enhancing scientific literacy in radio astronomy. It highlights flagship programs such as the "Exploring the Cosmos" lecture series, the "SKAIC Young Astronomers Program," and community sky observation events. The study emphasizes the alignment of EPO activities with ongoing research, fostering public engagement and curiosity in scientific inquiry. Through collaborative efforts, SKAIC aims to cultivate a scientifically literate society, bridging the gap between advanced astronomical research and public understanding of the universe.
| Published on 11 Feb 2024
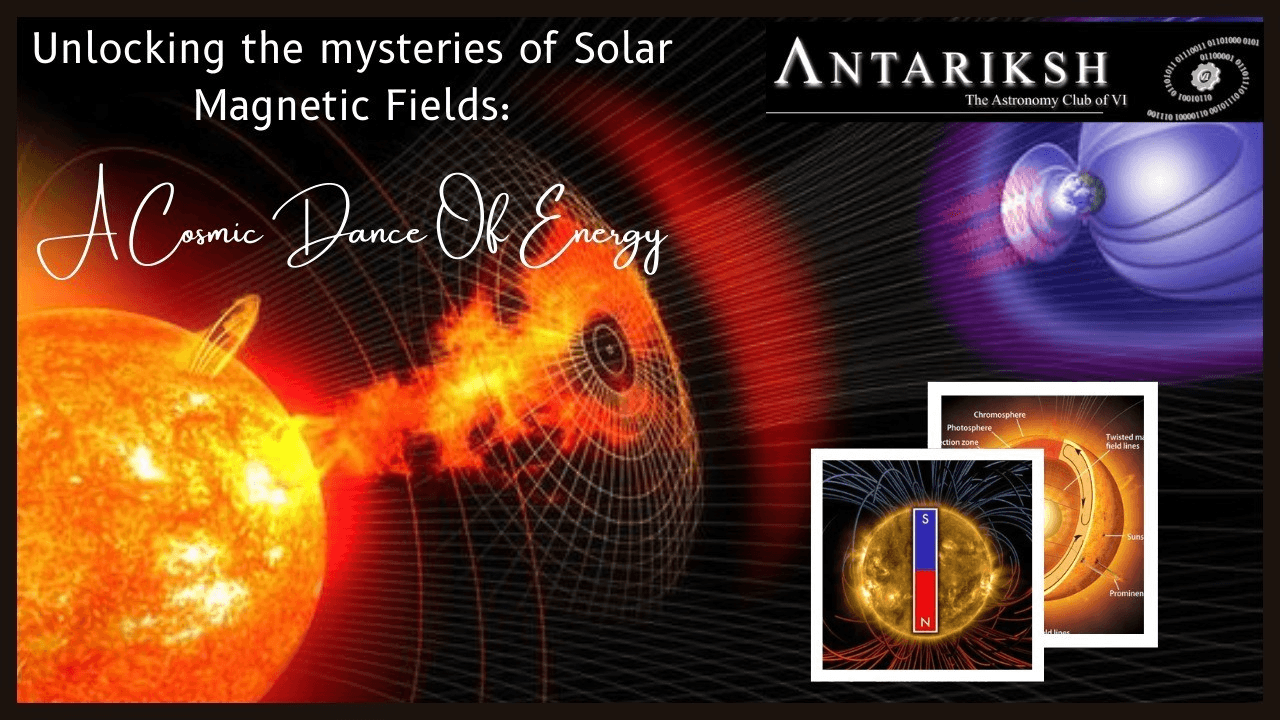
Unlocking the Mysteries of Solar Magnetic Fields: A Cosmic Dance of Energy!
This study investigates solar magnetic fields (SMF) and their interactions with solar winds and sunspots. The SMF, generated by solar dynamo processes, plays a crucial role in maintaining solar system stability and influences space weather phenomena, including geomagnetic storms on Earth. By analyzing the properties of SMF and their effects on Earth’s magnetosphere, the research highlights the significance of these magnetic fields in protecting the solar system from cosmic radiation. The findings emphasize the importance of continued exploration of solar magnetic dynamics for understanding broader astrophysical processes.
| Published on 08 Feb 2024

Image Archives
| Published on 03 Feb 2024

Theories of Habitable Exoplanets
On February 3, 2024, Antariksh VI held an internal talk at VIT Pune on "Theories of Habitable Exoplanets," led by Kaushik Salunke. The session explored exoplanet types, detection methods like transit photometry and Doppler spectroscopy, and key examples, such as TRAPPIST-1e and Kepler-452b. Criteria for habitability—like the presence of water, stable atmospheres, and magnetic fields—were discussed, alongside challenges in analyzing distant atmospheres and technological constraints. The talk concluded with a focus on future missions seeking biosignatures and the need for advanced technologies. Participants appreciated the session, suggesting more research-focused insights into this exciting field.
| Published on 01 Feb 2024

History and Working of Optical Telescopes
On January 13, 2024, the Antariksh Astronomy Club of VIT Pune hosted a talk on the "History and Working of Optical Telescopes," presented by Bhavya Shah. Covering telescope types—refractive, reflective, and catadioptric—the talk explored key models like Galilean, Keplerian, and Schmidt-Cassegrain telescopes, highlighting advantages, challenges, and optical aberrations such as chromatic and geometric distortions. Mount types, including Dobsonian and equatorial, were discussed for their tracking capabilities and suitability in astrophotography. The session provided attendees with a foundational understanding of telescope mechanics and advancements, emphasizing telescopes' pivotal role in astronomical observations.
| Published on 12 Jan 2024

3D Mapping of Our Universe: Using Stellar parallax
This article delves into the parallax method, a fundamental technique in astronomy for determining the distances to stars. It provides a historical perspective on stellar parallax measurements, starting with Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel's groundbreaking work on 61 Cygni in 1838. The article discusses various parallax measurement techniques, including ground-based optical and near-infrared observations, and advanced methods like Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) in radio astronomy. Additionally, it highlights the significant contributions of the Hipparcos and Gaia missions in creating a comprehensive 3D map of the Milky Way, enhancing our understanding of stellar distances and distributions.
| Published on 31 Dec 2023